Introduction to Data Culture
A successful data culture is the cornerstone of any modern business aiming to thrive in today’s data-driven world.
In the end, how are automated data pipelines, other data infrastructure and BI reports and dashboards useful if the end user does not know why it is important, and does not know how to interpret the information?
So, what exactly does a data culture entail, and how can businesses implement it effectively?
Key Components of a Data Culture
Let’s try to break down data culture in its components. What is needed to implement a successful data culture?
Data Governance
Establish clear policies to manage data quality, privacy, and security, aligning with organizational objectives. Mature companies have data strategies in place for this purpose, but it does not need to be a full data strategy from the beginning. Make sure that data is properly managed by assigning data stewards for specific domains. For example, nominate one person in the HR team that oversees the use of HR data across the company. Furthermore, educate report builders and people working with data, how the information is to be used.
Access to Data
Ensure relevant, high-quality data is accessible to all employees who need it, fostering transparency and trust. Make sure that data quality assuranc processes are in place and the time & effort required to gain access to information, is as frictionless as possible – without compromising data security. Again, something a data steward can take care of.
Data Literacy
Equip employees with the skills to understand and leverage data effectively. This involves educating teams about interpreting and applying data insights in their daily tasks. Furthermore, make sure the employees understand the importance of KPIs and how they are measured.
Standardized Communication
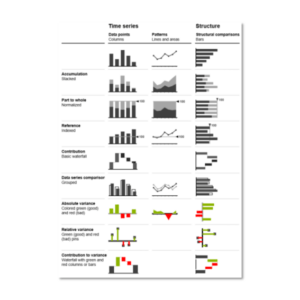
Use frameworks like the International Business Communication Standards (IBCS) to ensure data visualization and reporting are clear, concise, and consistent across the organization.
Steps to Implement a Data Culture
Nominate the right people, start small
Nominate roles such as data stewards to start leveraging data more across the entire organization. Train data stewards about some ground rules for using data in your organization. Again, it does not need to be a full data strategy from the beginning, but this will give you a solid foundation to start developing one for your organization! Learn as you go and start building that strategy.
Educate and Train
Develop a comprehensive data literacy program that includes workshops, e-learning modules, or mentorship opportunities. Provide resources such as books, articles, and internal knowledge libraries to promote ongoing learning. Hot tip: Use formats like a brown-bag lunch to educate employees while making it a fun experience.
Foster Collaboration
Encourage cross-departmental collaboration on data projects to break down silos and share best practices. This can be aligned with a Power BI Governance or other company wide initiatives. For example, use concrete problems in your organization and build cross functional project teams that will try to solve this problem using data & analytics.
Adopt and implement Effective Tools
Implement platforms like Power BI, which can be deployed quickly and at a low cost, to facilitate data analysis and visualization across many different sources. Power BI can be looked at as the “PowerPoint for data” as it is rather easy to use, and democratizes the use of data across your organization. However, be sure to set up a proper Power BI Governance while doing so! Be sure to also check out our other blogpost around Power Bi Governance: Key aspects for a successful Power BI Governance
Centralize KPI Definitions
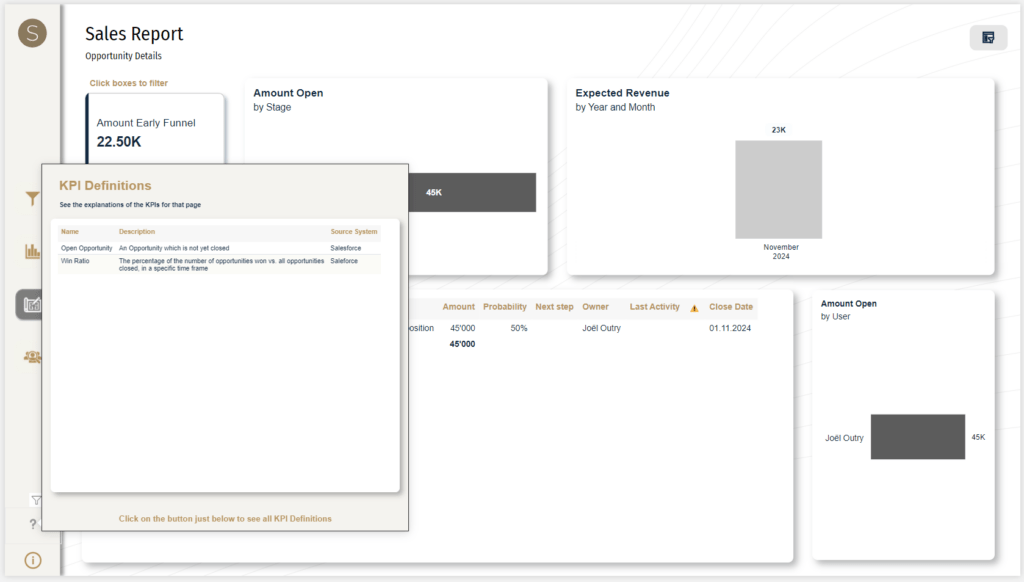
I can’t stress this enough! Start collecting and defining your KPIs in a centralized place where everyone has access to. You can use any tool of your choice, but preferably it does not sit in an isolated Word File or PDF. Instead, use tools like SharePoint Lists, Confluence or Excel (if really necessary 😉). The main benefit: You can bring those KPI Definitions into your Power BI as a data source and start using it in all your reports. For example: Use custom tooltips to show the definitions of the KPIs in a specific visual or report page!
Furthermore, make sure you set up a KPI Framework that focuses on the relevant KPIs for each team, while connecting them to the company’s objectives!

Evaluate and Adapt
Regularly assess the organization’s data culture through feedback and performance metrics. Use tools like Sparke Consulting’s maturity model to identify areas for improvement. Only by constantly re-evaluating your programs ad frameworks can you build something that generates values and fits to your organization. Note: there’s no one-size fits all data culture. Every organization has its unique challenges which need to be addressed when setting up a data culture!
Benefits of a Strong Data Culture
- Improved Decision-Making: Employees can base decisions on reliable, accurate data rather than intuition or outdated methods.
- Enhanced Innovation: Data-driven insights open new avenues for creativity and problem-solving.
- Employee Engagement: Empowering teams with data literacy and visibility into how their work impacts the business creates a motivated workforce. Especially when you have KPIs that are aligned with the company objectives!
Implementing IBCS Standards
Adopting IBCS standards ensures that your data communication is not only professional but also impactful. These standards emphasize clarity and consistency, making it easier for all stakeholders to understand data-driven insights and act on them.
Conclusion
Building a successful data culture is not just about tools and technology—it’s about people, processes, and strategy. By aligning data culture initiatives with business objectives, fostering collaboration, and implementing governance frameworks like IBCS and Power BI, organizations can create an environment where data drives every decision.
Sparke Consulting specializes in helping businesses establish and enhance their data culture. Contact us today to take the first step toward a data-driven future.